Osmotic Pumps

The osmotic pump has become the best tool for continuous dose of unrestrained laboratory animals. It can be implanted subcutaneously or intraperitoneally in animals. Minimizes side effects and experimental variables, and reduces the risk of stress due to frequent animal handling. And it is used for continuous delivery of a wide range of drugs, including antibodies, growth factors, cytokines, chemotherapeutics, addictive drugs, hormones, steroids and more. Features: Ensure continuous and uninterrupted administration, maintaining the preset speed for the administration of the animal. Storage capsules have good drug compatibility, and protection for short half-life drugs. Capsules have good biocompatibility and do not affect the physiology of animals. Easy to use, It allows one-time operation in an experiment instead of frequent operation. Avoid the stress caused by repeated administration, reducing the impact of non-experimental factors on the experimental results. Small size, can be applied to experiments on mice, neonatal rats and other small animal. Ensure that the drug is delivered to the target site accurately.
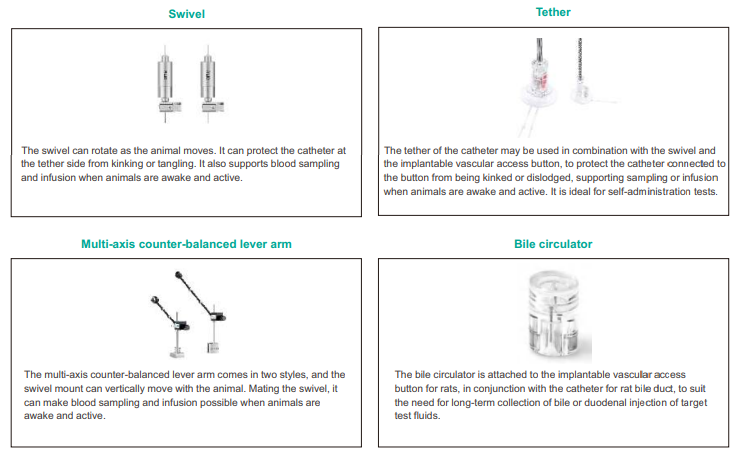
The osmotic pump can be directly implanted in the abdominal cavity or the back of the neck for drug administration, or it can be applied to specific tissue and organ, such as blood vessels, brain, spinal cord, subcutaneous part, abdominal cavity, etc., by connecting the catheter or other accessories.

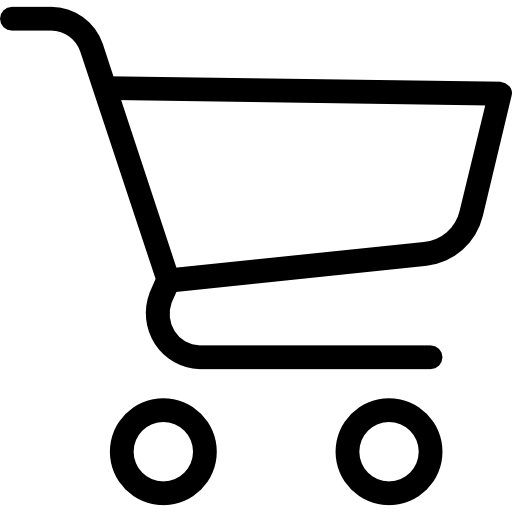
Flow regulator: The sole outlet for drug solution, which is used to connect the catheter to target administration area.
Storage capsules: Fill with solution. It has good corrosion resistance to acid and alkali.
Salt interlayer: absorption of tissue fluid by osmosis. After the salt interlayer absorbs the tissue fluid, it can only be extruded inwards to slowly pump the solution out of the capsule.
Pellicle: prevents the salt layer from diffusing into the tissue, and ensures that the tissue fluid can enter the salt layer to squeeze the storage capsule and pump out the drug solution